Introduction
Cyber security for beginners is one of the most important topics in today’s digital world. Almost everything we do now depends on the internet, from online learning and shopping to banking and social media. Because of this heavy dependence, cyber threats are increasing every day. Hackers, scammers, and cybercriminals are always looking for new ways to steal data, money, and personal information. That is why learning cyber security for beginners is no longer optional. It is a basic life skill.
Many people think cyber security is only for experts or IT professionals. In reality, anyone who uses a smartphone, laptop, or the internet needs basic cyber security knowledge. Beginners often feel confused by technical terms and complex explanations. However, cyber security does not have to be difficult. With simple concepts and practical steps, anyone can understand how to stay safe online.
This guide on cyber security for beginners is written in simple English for easy understanding. It is designed for students, professionals, and everyday internet users who want to protect themselves. You will learn what cyber security means, why it is important, and how you can apply it in daily life. Real-world examples are included to make concepts clear.
By the end of this article, you will have a strong foundation in cyber security for beginners. You will know how to protect your devices, data, and online identity. Most importantly, you will feel more confident and aware while using the internet in your daily routine.
What is Cyber Security for Beginners?
Cyber security for beginners refers to the basic practices and knowledge used to protect computers, networks, mobile devices, and data from digital attacks. These attacks are usually aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information. Cyber security also focuses on preventing unauthorized access and ensuring safe online behavior.
In simple words, cyber security means staying safe in the digital world. Just like we lock our homes to stay safe, cyber security helps lock our digital life. This includes protecting passwords, personal details, emails, photos, and financial information.
Cyber security covers many areas such as network security, data protection, application security, and user awareness. For beginners, the focus is mainly on understanding common threats and learning how to avoid them. Examples of cyber threats include viruses, phishing emails, ransomware, and identity theft.
Cyber security for beginners also involves learning safe habits. These habits include creating strong passwords, updating software regularly, and avoiding suspicious links. Even simple actions can greatly reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
Understanding cyber security basics helps beginners build a safe online environment. It is the first step toward responsible and secure internet usage in both personal and professional life.
Why is Cyber Security for Beginners Important?
Cyber security for beginners is important because cyber threats can affect anyone, regardless of age or profession. Hackers do not only target big companies. Individuals are often easier targets because they lack awareness.
One major reason cyber security is important is data protection. Personal data such as phone numbers, addresses, and bank details are valuable to cybercriminals. Once stolen, this data can be misused for fraud or identity theft.
Another reason is financial safety. Online scams and fake websites can trick beginners into sharing credit card details or sending money. Cyber security knowledge helps identify and avoid such scams.
Cyber security for beginners is also important for privacy. Many apps and websites collect user data. Without proper security, this data can be exposed or sold without permission.
In addition, cyber attacks can cause emotional stress and loss of trust. Recovering from a hacked account or stolen identity can take months. Learning cyber security basics helps prevent these situations before they happen.
Overall, cyber security awareness creates a safer digital experience. It empowers beginners to use technology confidently and responsibly without fear.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
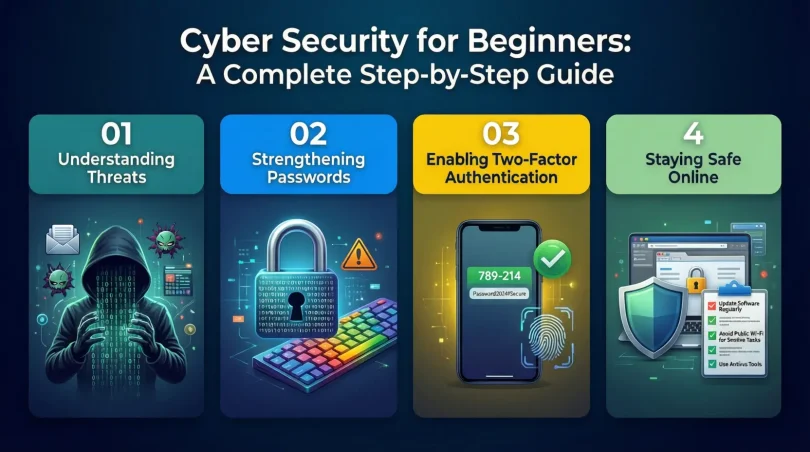
Step 1: Understand Common Cyber Threats
The first step in cyber security for beginners is understanding common threats. Viruses are harmful programs that damage files or systems. Phishing attacks use fake emails or messages to steal information. Malware includes spyware and ransomware that can lock or monitor devices.
Knowing these threats helps beginners recognize danger signs early. Awareness is the strongest defense against cyber attacks.
Step 2: Create Strong and Unique Passwords
Passwords are the first line of defense. Beginners should avoid using simple passwords like names or birthdates. A strong password includes letters, numbers, and symbols.
Using different passwords for different accounts is also important. If one account is hacked, others remain safe. Password managers can help store passwords securely.
Step 3: Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. It requires a second verification step, such as a code sent to your phone. Even if someone steals your password, they cannot access your account easily.
Cyber security for beginners strongly recommends enabling this feature wherever available.
Step 4: Keep Software and Devices Updated
Software updates fix security weaknesses. Many beginners ignore updates, but this can leave devices vulnerable. Always install updates for operating systems, apps, and antivirus programs.
Updated software reduces the risk of cyber attacks and improves device performance.
Step 5: Use Antivirus and Security Tools
Antivirus software helps detect and remove threats. Beginners should install trusted security tools and keep them updated. Firewalls also help block unauthorized access.
These tools work silently in the background to protect your system.
Step 6: Practice Safe Browsing Habits
Avoid clicking on unknown links or downloading files from untrusted sources. Check website URLs carefully before entering personal information. Secure websites usually start with “https”.
Safe browsing is a key habit in cyber security for beginners.
Step 7: Protect Personal Information Online
Do not share personal details on public platforms. Limit what you post on social media. Review privacy settings regularly to control who can see your information.
Protecting personal data reduces the risk of identity theft.
Step 8: Backup Important Data Regularly
Data backups help recover files in case of cyber attacks or device failure. Use external drives or cloud storage for backups. Regular backups ensure data safety.
This step is often ignored but is very important.
Benefits of Cyber Security for Beginners

- Protects personal and financial information
- Reduces the risk of online scams and fraud
- Builds confidence in using digital technology
- Enhances privacy and data safety
- Prevents unauthorized access to accounts
- Saves time and money by avoiding cyber incidents
- Improves overall digital awareness
Disadvantages / Risks
- Requires time to learn basic concepts
- Some security tools may cost money
- Overconfidence can lead to careless behavior
- Poor configuration can reduce effectiveness
- Constantly evolving threats require ongoing learning
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many beginners make simple mistakes that increase risk. Using the same password everywhere is a common error. Ignoring software updates is another major mistake.
Clicking on suspicious links without checking sources is also risky. Sharing too much personal information online can attract cybercriminals.
Some beginners rely only on antivirus software and ignore safe habits. Cyber security for beginners requires both tools and awareness.
Avoiding these mistakes can significantly improve online safety.
FAQs
What is cyber security in simple words?
Cyber security means protecting your digital devices and information from online threats. It helps keep data safe from hackers.
Is cyber security hard to learn for beginners?
No, cyber security for beginners is easy if learned step by step. Basic habits and awareness are enough to stay safe.
Do beginners need antivirus software?
Yes, antivirus software helps detect and block threats. It is an important tool for beginners.
Can cyber attacks happen to normal users?
Yes, anyone using the internet can be targeted. Beginners are often easier targets due to lack of awareness.
How often should passwords be changed?
Passwords should be changed every few months or immediately after a security breach.
Is cyber security only for computers?
No, cyber security also applies to smartphones, tablets, and online accounts.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
Experts suggest staying updated with cyber security trends. Always think before clicking on links. Use secure Wi-Fi networks and avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive tasks.
Regularly review account activity for unusual behavior. Educate family members about basic cyber security for beginners. Awareness at home increases overall safety.
Developing a security-first mindset is the best long-term strategy.
Conclusion
Cyber security for beginners is a vital skill in the modern digital age. As technology continues to grow, so do cyber threats. Beginners who understand basic cyber security concepts are better prepared to protect themselves. This guide has explained cyber security in simple terms, making it easy to understand and apply.
By following step-by-step practices such as creating strong passwords, updating software, and browsing safely, beginners can reduce risks significantly. Cyber security is not about fear but about awareness and smart habits. Even small actions can make a big difference in online safety.
Learning cyber security for beginners also builds confidence. When users know how to protect their data, they can enjoy technology without worry. It empowers individuals to take control of their digital lives.
In conclusion, cyber security is everyone’s responsibility. Start with the basics, stay informed, and practice safe online behavior daily. With the right knowledge and habits, beginners can create a secure and stress-free digital experience for themselves and others.