Introduction
In today’s digital age, cyber security threats have become one of the most critical concerns for individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. As technology advances rapidly, so do the tactics used by cybercriminals. From personal computers and mobile devices to large corporate networks, no system is completely safe. Cyber attacks can lead to financial loss, privacy breaches, and even damage a company’s reputation. Therefore, understanding cyber security threats is no longer optional—it is a necessity for everyone who uses technology.
Cyber security threats come in many forms, including malware, phishing attacks, ransomware, and social engineering. These threats are constantly evolving, making it essential to stay informed about the latest methods hackers use. A single security lapse can have devastating consequences, but with proper knowledge and precautionary measures, these risks can be significantly minimized. This guide will explain what cyber security threats are, why they are important, and how you can protect yourself and your organization.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of cyber security threats, common mistakes to avoid, expert tips for protection, and the benefits of maintaining strong digital security practices. Whether you are a beginner wanting to learn the basics or an intermediate user looking to enhance your cyber security knowledge, this guide will help you navigate the complex world of online threats confidently.
What is Cyber Security Threats?
Cyber security threats are malicious activities or attacks aimed at gaining unauthorized access to computers, networks, or digital information. In simple terms, these threats are actions by cybercriminals intended to harm individuals, businesses, or even governments. Cyber threats can target personal data, financial information, sensitive business files, or critical infrastructure systems.
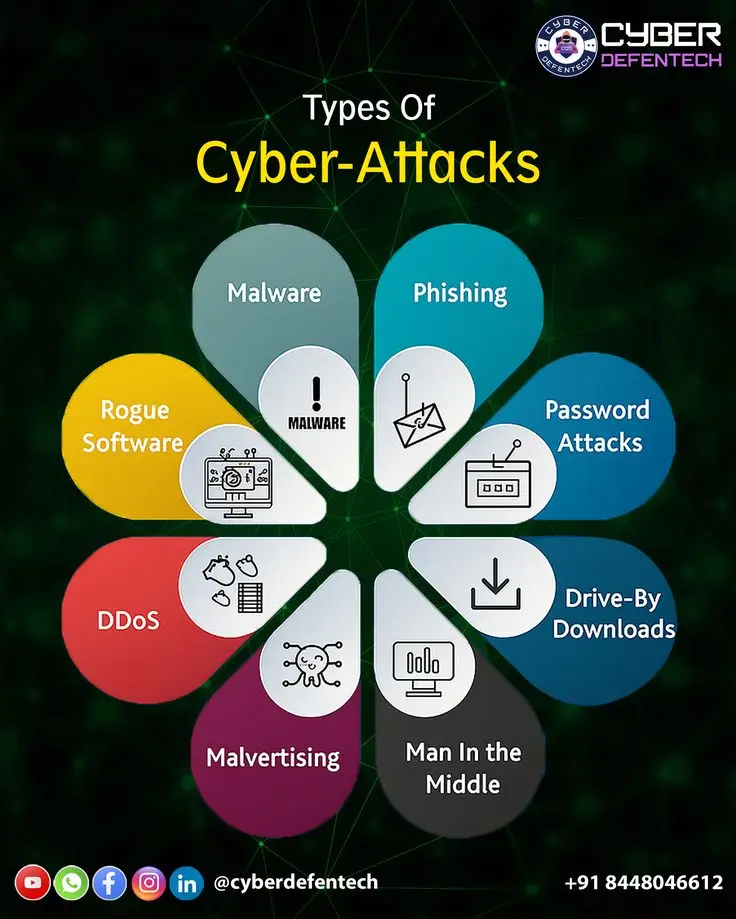
There are several types of cyber security threats, including:
- Malware: Malicious software designed to damage or disrupt systems.
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Ransomware: A type of malware that locks users’ files until a ransom is paid.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals to gain confidential information.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Overloading systems to make them unavailable.
- Spyware: Software that secretly monitors and collects information from users.
The primary goal of these threats is often financial gain, data theft, or sabotage. For organizations, cyber security threats can disrupt operations, harm reputation, and result in significant financial losses. For individuals, threats can lead to identity theft, loss of personal data, and even emotional stress.
Understanding the nature of cyber security threats is the first step in preventing them. Awareness helps users identify suspicious activities and take proactive measures to safeguard their digital environment.
Why is Cyber Security Threats Important?
The importance of understanding cyber security threats cannot be overstated. With the increasing reliance on technology, almost every aspect of modern life is connected to digital systems. From online banking and shopping to remote work and cloud storage, the risks of cyber attacks are everywhere.
Key reasons why cyber security threats are important:
- Protection of Personal Data: Cyber threats often aim to steal personal information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or social security details. Protecting this data is essential to prevent identity theft and financial loss.
- Business Continuity: For companies, a cyber attack can disrupt operations, halt productivity, and lead to loss of revenue. Ensuring robust cyber security helps maintain uninterrupted business activities.
- Reputation Management: Organizations affected by cyber attacks may lose customer trust. Customers value businesses that prioritize security.
- Legal Compliance: Many industries have strict regulations regarding data protection. Failing to secure systems can result in fines and legal consequences.
- National Security: Cyber attacks on government systems or critical infrastructure can have wide-ranging effects, impacting millions of people.
In essence, understanding cyber security threats is not just a technical necessity but a strategic requirement for safeguarding digital life. Being aware of these threats allows individuals and organizations to implement effective security measures and reduce the risk of attacks.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide to Cyber Security Threats
Protecting yourself or your organization from cyber security threats requires a systematic approach. Below is a step-by-step guide to understanding and mitigating these threats.
Step 1: Identify the Types of Threats
The first step in cyber security is to know what you are up against. Common threats include:
- Malware: Viruses, worms, trojans, and spyware.
- Phishing: Fake emails, messages, or websites designed to steal information.
- Ransomware: Blocks access to files and demands payment for recovery.
- Denial of Service (DoS): Flooding networks to disrupt services.
- Insider Threats: Employees or associates misusing access privileges.
Step 2: Evaluate Vulnerabilities
Conducting a vulnerability assessment helps identify weak points in your system:
- Review software and operating systems for updates.
- Check network configurations.
- Assess password policies and access controls.
- Evaluate employee awareness and training levels.
Step 3: Implement Security Measures
After identifying threats and vulnerabilities, apply the following protective measures:
- Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Protects against malware and malicious files.
- Use Firewalls: Monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic to block unauthorized access.
- Regular Updates: Keep operating systems, apps, and software updated to patch security holes.
- Strong Passwords: Use complex passwords and change them regularly.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of security for accounts.
Step 4: Educate Users
Human error is one of the biggest causes of cyber security breaches. Educating users reduces risks:
- Train employees on phishing and social engineering tactics.
- Encourage safe browsing habits.
- Promote awareness of suspicious emails or downloads.
Step 5: Monitor and Respond
Continuous monitoring is essential to detect and respond to cyber threats quickly:
- Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor unusual activities.
- Establish an incident response plan for quick action.
- Regularly review security logs and alerts.
Step 6: Backup and Recovery
Even with strong security, breaches may occur. Having a reliable backup strategy ensures minimal impact:
- Perform regular backups of critical data.
- Store backups in multiple locations (cloud + offline storage).
- Test backup recovery procedures periodically.
Step 7: Continuous Improvement
Cyber threats evolve constantly. Regularly review and improve your security measures:
- Conduct periodic security audits.
- Update security policies.
- Stay informed about new cyber threat trends.
Benefits of Cyber Security
Implementing robust cyber security measures provides numerous advantages:
- Data Protection: Safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Financial Security: Prevents monetary losses due to fraud or ransomware.
- Customer Trust: Enhances credibility and loyalty by ensuring privacy and security.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet legal requirements and avoid penalties.
- Business Continuity: Reduces downtime and operational disruptions.
- Peace of Mind: Reduces stress related to cyber threats.
Disadvantages / Risks of Cyber Security Threats
Despite security measures, cyber threats come with risks:
- Financial Loss: Cyber attacks can result in costly damages.
- Data Breach: Sensitive data may be stolen or leaked.
- Reputation Damage: Public trust can be affected after an incident.
- Operational Disruption: Attacks can halt normal business activities.
- Legal Consequences: Failure to protect data can result in fines.
- Constant Vigilance Needed: Maintaining security requires ongoing effort.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To minimize cyber security risks, avoid these common mistakes:
- Weak Passwords: Using simple or reused passwords increases vulnerability.
- Ignoring Updates: Delaying software and system updates exposes systems to threats.
- Lack of Backups: Not backing up data can result in permanent loss during attacks.
- Falling for Phishing: Clicking on suspicious links can compromise accounts.
- Insufficient Training: Employees unaware of security protocols are high-risk targets.
- Overlooking Mobile Security: Smartphones and tablets often get less protection but can be entry points for attackers.
FAQs About Cyber Security Threats
1. What is the most common type of cyber security threat?
The most common threats are malware and phishing attacks. Malware infects systems to steal information or damage files, while phishing tricks users into giving sensitive information.
2. How can I protect my personal data online?
Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, update software regularly, and avoid sharing sensitive information on suspicious websites.
3. What is ransomware, and how does it work?
Ransomware is malicious software that locks your files or system until you pay a ransom. It spreads through infected emails, downloads, or compromised websites.
4. Can small businesses face cyber attacks?
Yes, small businesses are often targeted because they may have weaker security measures. Protecting systems and training employees is crucial.
5. How do I know if my system is under attack?
Signs include slow performance, unexpected pop-ups, unauthorized logins, and unusual network activity. Intrusion detection systems can help monitor threats.
6. Is antivirus software enough to prevent cyber threats?
No, antivirus is important but not enough. Use firewalls, regular updates, backups, and employee training to strengthen security.
7. What is social engineering in cyber security?
Social engineering involves manipulating people to reveal confidential information, often via phishing, phone calls, or fake websites.
8. How often should I update my passwords?
It is recommended to update passwords every 2–3 months and avoid reusing old passwords across multiple accounts.
9. Are public Wi-Fi networks safe?
Public Wi-Fi is risky because hackers can intercept your data. Use VPNs and avoid logging into sensitive accounts on public networks.
10. What are insider threats?
Insider threats come from employees or associates who misuse access privileges, intentionally or accidentally compromising security.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
To stay ahead of cyber security threats, follow these expert tips:
- Use Multi-Layered Security: Combine antivirus, firewalls, and monitoring systems for stronger protection.
- Regularly Conduct Security Audits: Identify vulnerabilities before hackers do.
- Educate Everyone: Make security awareness a part of your company culture.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Ensure that stolen data cannot be easily read.
- Limit Access: Only provide access to data and systems necessary for job roles.
- Use VPNs for Remote Work: Secure communication channels for employees working from home.
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to cyber security news and threat alerts.
Bonus points: Regularly test your system’s security using penetration testing and simulate phishing attacks to prepare employees for real-world scenarios.
Conclusion
Cyber security threats are a reality that affects individuals, businesses, and governments alike. The rise of technology has created unprecedented opportunities, but it has also opened doors for cybercriminals. Understanding the types of threats, their risks, and how to prevent them is crucial for everyone in the digital world.
By implementing strong security measures such as antivirus software, firewalls, regular updates, strong passwords, backups, and employee training, you can significantly reduce the chances of a successful attack. Awareness and vigilance are your best defenses against cyber threats. Regular monitoring, audits, and staying informed about new risks ensure long-term protection.
Ultimately, cyber security is not just about technology; it is about creating a culture of safety and responsibility. Investing in cyber security today protects your data, your finances, and your reputation tomorrow. Whether you are an individual or part of an organization, proactive measures can save you from costly consequences and provide peace of mind in an increasingly connected world.





