Introduction
In today’s digital age, data protection methods are more important than ever. Every day, businesses and individuals generate a massive amount of data, including personal details, financial records, and sensitive business information. Protecting this data is not just a legal requirement in many cases—it is essential for maintaining trust, preventing financial losses, and avoiding cyber threats. Whether you are a beginner or have some experience with online security, understanding the basics of data protection can save you from costly mistakes.
Data breaches, malware attacks, and identity theft have become increasingly common, making the need for robust data protection methods critical. From encrypting sensitive files to using strong passwords and cloud backups, there are multiple ways to ensure that your information remains secure. Additionally, organizations must comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA, which further highlight the importance of safeguarding personal and professional data.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to data protection, including definitions, importance, step-by-step methods, benefits, risks, common mistakes, FAQs, and expert tips. By the end, you will be equipped with practical knowledge to protect your data effectively and confidently.
What is Data Protection?
Data protection refers to the process of safeguarding digital and physical information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft. It involves implementing measures that ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This includes personal information like names, addresses, and financial details, as well as organizational data such as client records, business strategies, and proprietary software.
At its core, data protection is about creating layers of security that prevent sensitive information from being compromised. Methods may include encryption, secure passwords, access controls, regular backups, and monitoring systems. The goal is to ensure that only authorized users can access the data while keeping it safe from cybercriminals and accidental loss.
In short, data protection methods are a combination of technical, organizational, and legal strategies designed to keep information safe in an increasingly digital world.
Why is Data Protection Important?
Data protection is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevent Financial Losses: Data breaches can lead to significant financial damages, including fines, compensation, and operational disruption.
- Maintain Trust: Clients and customers trust businesses to handle their information responsibly. A breach can damage your reputation permanently.
- Legal Compliance: Many countries have strict regulations regarding personal data. Failing to protect data can result in legal penalties.
- Prevent Cybercrime: Strong protection methods reduce the risk of hacking, ransomware, and phishing attacks.
- Ensure Business Continuity: Losing critical data can halt business operations. Regular backups and secure storage keep businesses running smoothly.
- Protect Personal Privacy: Individuals need data protection to prevent identity theft and unauthorized access to personal information.
In summary, whether you are a small business or an individual, implementing effective data protection methods is essential to ensure security, trust, and operational stability.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide to Data Protection Methods

Here is a practical guide to protecting your data efficiently:
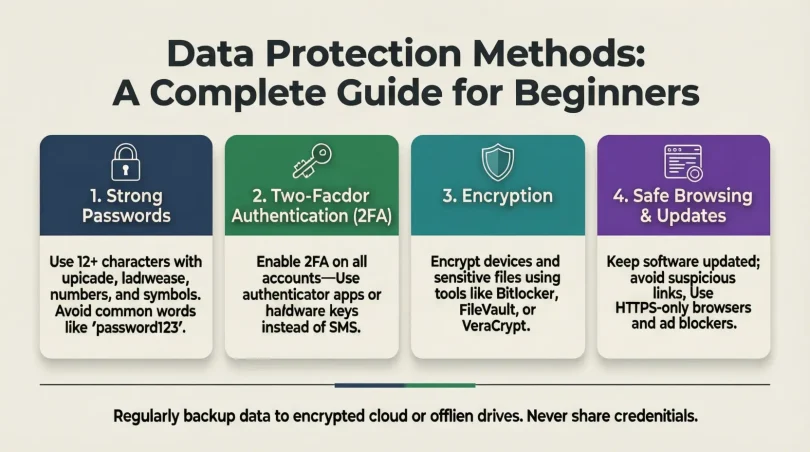
1. Use Strong Passwords and Authentication
- Create unique passwords for every account.
- Use a combination of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols.
- Consider multi-factor authentication (MFA) for extra security.
- Avoid using easily guessable passwords like birthdays or “123456”.
2. Encrypt Sensitive Data
- Encrypt files, emails, and databases to make information unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Use end-to-end encryption for messaging apps.
- Consider encryption tools such as VeraCrypt or BitLocker.
3. Regular Backups
- Schedule regular backups of important files.
- Store backups in multiple locations (cloud and physical storage).
- Test backups periodically to ensure they are accessible and functional.
4. Update Software and Systems
- Keep operating systems, antivirus software, and applications up-to-date.
- Install security patches immediately after release.
- Avoid using outdated software that may contain vulnerabilities.
5. Use Antivirus and Anti-Malware Programs
- Install reliable antivirus software on all devices.
- Perform regular scans to detect and remove threats.
- Enable real-time protection to block malicious activities.
6. Secure Network Connections
- Use strong Wi-Fi passwords and change them regularly.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions.
- Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for secure browsing.
7. Limit Data Access
- Grant access only to authorized personnel.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) in organizations.
- Monitor access logs to detect unusual activities.
8. Safely Dispose of Data
- Shred physical documents containing sensitive information.
- Securely delete digital files using specialized software to prevent recovery.
- Avoid disposing of devices without wiping data completely.
9. Educate Yourself and Your Team
- Conduct regular training on phishing, password hygiene, and safe browsing.
- Stay informed about the latest cyber threats and scams.
- Encourage a security-conscious culture in your organization.
10. Implement Cloud Security Measures
- Choose cloud providers with strong security protocols.
- Use encryption and access controls for cloud-stored data.
- Regularly audit cloud accounts to detect any security gaps.
Benefits of Data Protection Methods
- Prevents Data Loss: Protects against accidental deletion or corruption.
- Enhances Privacy: Safeguards personal and sensitive information.
- Reduces Cyber Threats: Minimizes the risk of hacking and malware attacks.
- Maintains Compliance: Ensures adherence to data protection laws and standards.
- Boosts Customer Trust: Clients feel confident sharing information with secure organizations.
- Supports Business Continuity: Keeps operations running during data incidents.
Disadvantages / Risks
- High Cost: Some data protection tools and services can be expensive.
- Complexity: Advanced encryption and security systems can be difficult for beginners.
- Human Error: Even with strong measures, mistakes like weak passwords can compromise security.
- False Sense of Security: Over-reliance on technology may lead to negligence in following safe practices.
- Data Accessibility Issues: Overly strict access controls may hinder authorized users from accessing needed data.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using Weak Passwords: Avoid simple passwords and reuse across accounts.
- Ignoring Updates: Not updating software increases vulnerability to attacks.
- Skipping Backups: Losing unbacked-up data can be disastrous.
- Falling for Phishing Scams: Always verify suspicious emails or messages.
- Neglecting Physical Security: Devices and documents should be protected physically as well.
- Overlooking Employee Training: Employees unaware of security risks can compromise the entire system.
FAQs About Data Protection Methods
Q1. What is the most effective data protection method?
The most effective method combines strong passwords, encryption, regular backups, and network security. A multi-layered approach is always safer than relying on a single method.
Q2. How often should I back up my data?
Critical data should be backed up daily or weekly, depending on how frequently it changes. Always keep multiple backup copies in different locations.
Q3. Is cloud storage safe for sensitive data?
Yes, if you use reputable cloud providers with encryption and strong access controls. However, sensitive data should always be encrypted before uploading.
Q4. What is encryption, and why is it important?
Encryption converts data into unreadable code for unauthorized users. It is crucial for protecting sensitive information like financial records and personal data.
Q5. Can antivirus software alone protect my data?
No, antivirus software is just one layer of protection. You also need backups, encryption, secure passwords, and safe browsing practices.
Q6. What should I do if my data is breached?
Immediately isolate affected systems, change passwords, notify relevant authorities or clients, and restore data from secure backups.
Q7. Are public Wi-Fi networks safe for accessing sensitive data?
Public Wi-Fi is generally unsafe. If necessary, use a VPN to secure your connection and avoid logging into critical accounts.
Q8. How can small businesses implement data protection efficiently?
Start with basic measures like strong passwords, employee training, regular backups, and antivirus software. Gradually implement advanced tools like encryption and access controls.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
- Use a Password Manager: Tools like LastPass or 1Password help create and store complex passwords.
- Monitor Accounts Regularly: Keep an eye on unusual activity in financial and cloud accounts.
- Secure Mobile Devices: Use lock screens, encryption, and remote wipe capabilities.
- Consider Data Masking: Hide sensitive data in databases for testing and development environments.
- Practice Least Privilege Principle: Only give access to data that a user absolutely needs.
- Regularly Review Security Policies: Update company or personal security policies to address new threats.
Conclusion
Protecting your data is no longer optional—it is a necessity in the digital world. Implementing strong data protection methods ensures that your personal and organizational information remains secure from cyber threats, accidental loss, and unauthorized access. From encryption and regular backups to strong passwords and employee training, there are many practical steps that anyone can take to safeguard their data.
While the process may seem complex at first, starting with small, manageable steps can build a solid foundation for data security. Over time, these methods create a secure digital environment that protects not only your information but also your trustworthiness, legal compliance, and peace of mind. By understanding the importance, risks, and best practices, you can confidently protect your data in an ever-evolving digital landscape.